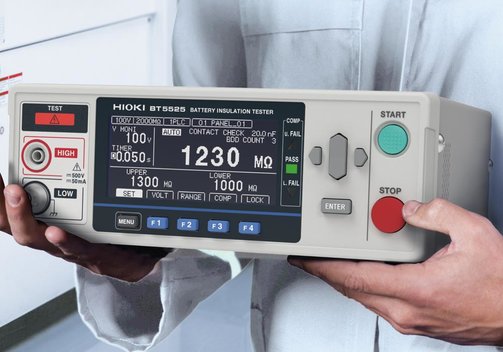
HIOKI BT5525 Battery Insulation Tester
Benefits of the BT5525 Tester with BBD and Insulation Resistance Testing
- Detect contamination that could cause defects.
- Improve battery cell productivity through high-speed testing.
- Ideal for insulation resistance testing before battery electrolyte filling.
HIOKI BT5525 Battery Insulation Tester
The HIOKI BT5525 is a versatile and fast battery insulation tester. The BDD (break down detect) function detects minuscule insulation defects caused by contamination and with this helps to prevent problems such as fires and accidents caused by heating after battery shipment as well as reduce battery degradation.
- Ideal for battery production lines.
- Detect minuscule insulation defects caused by contamination (BDD/break down detect function): Helps to prevent the risk of hazards such as fires and accidents caused by heating after battery shipment. Contributes to the production of batteries with greater durability and electrical performance, as minuscule internal short-circuits in cells accelerate battery degradation.
- Stable insulation resistance testing, even in noisy environments.
- Contact check function reduces the number of false negatives caused by equipment issues.
- Ideal for insulation resistance testing before battery electrolyte filling.
- Shorten cycle times with a maximum charging current of 50 mA.
- Compact dimensions make it easy to integrate the BT5525 into other systems.
- PC application for analyzing waveforms; with CSV-format data output.
- Applications: Manufacturers and system integrators of Li-ion batteries, small scale specialty Li-ion battery production.
Model Overview
| Model | BT5525 |
| Main test features | Insulation resistance test; break down detect function (BDD); contact check function |
| Output specifications | Output voltage 25...500 V, setting resolution 1 V; charging current (current limit function) 50 µA...50 mA (also see detailed specs in data sheet), min. setting resolution 10 µA; short-circuit current 60 mA or less; discharge current up to 40 mA |
| Measurement specifications | Resistance value display range 0.050...9999 MΩ; resistance ranges 2 MΩ, 20 MΩ, 200 MΩ, 2000 MΩ, AUTO |
| Basic specifications | ±1.5% rdg. ±2 dgt.; 25 V ≤ V < 100 V (0.05...2 MΩ),; 100 V ≤ V ≤ 500 V (0.2...20 MΩ) |
| Time specifications | Test time 0.050...999.999 s, OFF; comparator delay time 0.001...999.999 s, AUTO; display update speed 1 PLC; sampling time 1...100 PLC |
| Memory functions | Panel save function: Saves up to 15 sets of measurement conditions. Measured value memory function: Saves up to 999 measured values in the instrument's internal memory |
| Judgment functions | Test modes: Continuous test, PASS STOP, FAIL STOP; comparator function: UPPER_FAIL (measured value < upper limit value), PASS(upper limit value ≥ measured value ≥ lower limit value), LOWER_FAIL (measured value < lower limit value |
| Various functions | Break down detect function (BDD): Detecting minuscule insulation defects caused by contamination. Contact check function: 2-terminal capacitance measurement method. Automatic data output function: Automatic output of measurement results via communication interface after completion of test. Command monitor function: Screen display of commands being sent and received. External I/O monitor function: Screen display of output signal ON/OFF and input signal status. Analog output function: Converts measured values to 0...4 VDC and outputs |
| Interfaces | USB, LAN, RS232C, EXT I/O |
| Power supply | 100...240 VAC, consumption approx. 20 VA |
| Maximum rated power | 100 VA |
| Dimensions (mm) | 215 x 80 x 307 (excluding protruding parts), approx. 2.8 kg |
Included: Hioki BT 5525, power cord, EXT I/O male connector, EXT I/O connector cover, EXT I/O interlock cancellation jig, startup guide.
Leads, Accessories
| Model | Description |
| L2130 | Clip type lead red for BT5525, for HIGH terminal, banana/alligator clip, 1.5 m length |
| L2131 | Clip type lead black for BT5525, for LOW terminal, special triaxial/alligator clip, 1.5 m length |
| L2132 | Unterminated lead red for BT5525, for HIGH terminal, banana/cut wire, 5 m length |
| L2133 | Unterminated lead black for BT5525, for LOW terminal, special triaxial/cut wire, 5 m length |
| L9094 | Output cord for BT5525, memory recorder, display units CM7290/91 and similar products, 3.5 mm mini plug to 4 mm/banana, 1.5 m length |
| L9637 | RS232C cable, 9 pin-to-9 pin, 1.8 m length |
Frequently Asked Questions:
Question: What are the functions of HIOKI BT5525 and what are its advantages?
Answer: The BT5525 battery insulation tester detects breakdowns in the insulation/separator between the positive and negative electrodes of a battery due to micro contaminations (BDD/break-down detect function). The insulation resistance is measured. Features such as fast charge/discharge, a 2-wire contact check function and a high insensitivity to noise ensure convenient and safe use of the device.
Question: What is the difference between insulation testing and HiPot testing?
Answer: Insulation tests are performed in battery production before the high potential test. Before the electrolyte is filled, the insulation resistance between the anode and cathode is measured, as well as after filling with the electrolyte. In addition, safety tests can be performed at the end of the production line for modules and packs between the housing and the positive/minus poles of the battery. The insulation resistance is measured in this process. There is currently no standard for these measurements. Usually, the tester applies a DC voltage of approx. 200 V (output voltage HIOKI BT5525: 25...500 V).
During the high-voltage test/HiPot test, a voltage higher than the nominal voltage is applied to the DUT/device under test in order to detect any current leaks. This determines the breakdown voltage at a weak point. The leakage current is measured.
Question: What causes micro-shorts?
Answer: Micro-shorts are caused by tiny metal contaminated particles in the cell. These are created, for example, when the materials are cut to size. The separator forms the insulation between the anode and cathode. The contaminations cause micro-shorts, these lead to breakdowns and a defective separator. Conventional insulation testers - in contrast to the HIOKI BT5525 - do not detect these micro-defects due to low sampling speeds and rate the DUTs as "Pass" in the test. However, the micro-defects can lead to faster deterioration of the battery, self-discharge and, in the worst case, even fire.
Information on product safety:
Manufacturer:
HIOKI E.E. Corporation, 81 Koizumi Ueda, Nagano 386-1192/JPN
www.hioki.com
(EU branch Germany)
Last seen